What Is Google Opal and How Does It Work?

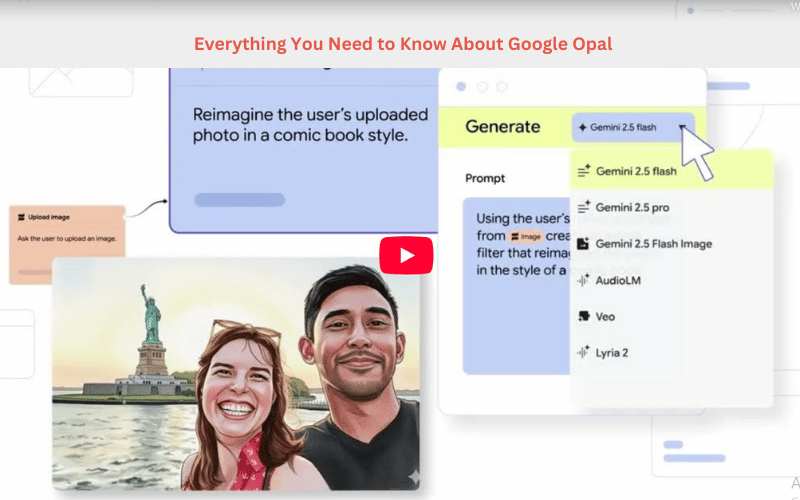
Google Opal is an experimental no-code AI workflow builder developed by Google Labs. It allows users to create AI-powered mini-apps and automations without writing traditional code.
In simple terms, you describe what you want, and Opal helps you visualise and chain together AI steps into an application.
Use cases include automating research, generating content, building internal productivity tools, or modelling a workflow that you’d otherwise have to script.
If you’re wondering “what is Google Opal, how does it work, and how much does it cost?” this guide covers everything you need to know about Google Opal’s features, uses, pricing, pros, and alternatives.
Where to Find Google Opal and What’s Its Pricing?

Availability
-
Originally launched in a U.S. public beta via Google Labs.
-
As of November 2025, Opal has expanded to over 160 countries.
So, depending on your region and account, you can access it at opal.google (or via the Google Labs interface).
Cost/Pricing
-
At the moment, Opal is free as part of its experimental/public-beta phase.
-
Google has not yet publicly committed to the eventual paid model, so “free now”, but that may change.
Access requirements
-
You’ll typically need a Google account.
-
Since it’s still experimental, features may be limited, geographies may vary, and Google may reserve the right to change access.
Google Opal Pros and Cons (2025 Overview)
Here are some of the key strengths and limitations based on current user feedback and reviews:
Pros
-
No coding required: One of the biggest draws is that you don’t need traditional programming experience.
-
Rapid prototyping: Helps convert a concept to a mini-app in minutes, useful for internal tools and experiments.
-
Visual workflow editor: Lets you build via drag-and-drop or natural-language prompts, chaining AI models and actions.
-
Uses Google’s AI models: Since it integrates with Google’s ecosystem (e.g., listings mention Gemini and other tools), it gives access to powerful underlying models.
-
Free (for now): Low barrier to entry, especially for non-technical teams wanting to experiment.
Cons
-
Experimental/early stage: Being in beta means features might be unstable, limited or subject to change.
-
Limited integrations: Some external APIs and system integrations may not yet be supported or are clunky.
-
Learning curve/usability issues: Even though it’s no-code, some users report that the interface and logic require adjustment.
-
Governance and security concerns: Rapid no-code app building can lead to “shadow IT” risk if not managed in a business context.
-
Undefined cost model for future: While free now, the transition to paid tiers might restrict some features or usage.
Best Alternatives to Google Opal

If you’re comparing Opal to other tools, here are notable alternatives:
-
Zapier: Workflow automation tool connecting many apps (good for task automation rather than full mini-apps).
-
Make (formerly Integromat): More visually oriented automation platform; flexible but steeper learning curve.
-
n8n: Open-source workflow automation; more control, more technical.
-
MindStudio/specialised AI agent builders: If you want AI agents rather than mini-apps.
-
Build your own with Google’s AI + custom dev: For full customisation and production-grade apps, you may still need developer work.
Each alternative has its niche: Opal focuses on rapid, no-code mini-apps leveraging Google’s AI models; others focus on automation, integration or more technical use cases.
Google Opal Uses: What You Can Build With It
Here are practical scenarios where Opal shines:
-
Rapid internal tool building: If your team needs a quick internal tool for workflow, summarising documents, or automating mundane tasks, Opal is a strong fit.
-
Prototyping ideas: If you have a concept for an AI-powered app or workflow, and want to test it quickly without full dev cost.
-
Non-technical teams wanting AI capability: Marketing, operations, and HR teams can build something useful without having to rely on engineering.
-
Experimentation: Since it’s free and accessible, you can experiment, fail fast, and learn how AI mini-apps might work in your organisation.
Where Opal Might Not Be the Right Fit (or Where Caution Applies)
-
Production-scale apps/enterprise-grade systems: If you need high scalability, complex integrations, full backend, or heavy customisation, you may need a more robust platform.
-
Strict security/governance environments: If you’re dealing with regulated data or need detailed audit trails/integrations, you’ll want strong oversight.
-
Cost-sensitive future planning: Because the pricing model isn’t locked in, relying solely on “free now” may risk future cost surprises.
-
Long-term support/contract commitments: As a beta tool, feature support, SLA, and availability may be less certain.
Summary
Google Opal is an exciting, no-code AI mini-app builder that opens doors for non-developers and teams wanting to prototype AI-enabled workflows quickly. It’s free in beta, supports over 160 countries, and integrates with Google’s AI model stack. However, as with many early-stage tools, there are trade-offs: limited integrations, some usability/learning curve challenges, and the unknown future pricing and enterprise maturity.
For organisations or individuals looking to experiment with AI mini-apps, it’s absolutely worth trying. But if you’re building a mission-critical, production system with heavy compliance or integrations, it may serve better as a prototyping path rather than the final platform.